Gastric bypass surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is a type of weight loss surgery that involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting the newly created pouch directly to the small intestine. After gastric bypass, swallowed food goes into this small stomach pouch and then directly into the small intestine, thus bypassing most of your stomach and the first part of your small intestine. Gastric bypass is one of the most common types of bariatric surgery. Gastric bypass is performed when diet and exercise have not worked or when you have serious health problems due to your weight.
Video of gastric bypass surgery
Preparation before gastric bypass surgery
In the weeks leading up to surgery, you may be asked to start an exercise program and stop smoking. Right before the procedure, you may have restrictions on what you eat and drink and what medications you can take. Now is a good time to plan ahead for your recovery after surgery.
When weight loss surgery doesn't work.
You may not lose enough weight or gain it back after weight loss surgery. This weight gain can happen if you don’t follow the recommended lifestyle changes. For example, if you frequently eat high-calorie foods, you may not lose enough weight. To prevent weight regain, you need to make permanent healthy changes to your diet and get regular physical activity and exercise.
It is important to keep all of your scheduled follow-up appointments after weight loss surgery so that your doctor can monitor your progress. If you notice that you are not losing weight or have complications after surgery, see your doctor right away.
Although gastric bypass surgery is widely performed, sleeve surgery is more useful and can have a greater effect on weight loss and maintenance.
Why gastric bypass?
surgery Gastric bypass is done to help lose excess weight and reduce the risk of potentially life-threatening weight-related health problems, including:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Type 2 diabetes
- Stroke
- Cancer
- infertility
Gastric bypass is usually only done after trying to lose weight by improving your diet and exercise habits.
Risks
As with any major surgery, gastric bypass and other weight loss surgeries carry potential health risks, both short-term and long-term.
Risks associated with surgery are the same as any abdominal surgery and can include: • Excessive bleeding
- Infection
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
- blood clotting
- Lung or breathing problems
- Leakage in your digestive system
Risks and long-term complications of gastric bypass can include the following:
- Ileus
- Dumping syndrome, which causes diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
- Gallstone
- Hernias
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Malnutrition
- Stomach perforation
- wounds
- Vomiting


Who is gastric bypass for?
In general, gastric bypass and other weight loss surgeries may be an option for you if:
- Your body mass index (BMI) is 40 or higher (severe obesity)
- Your BMI is 35 to 39.9 (obese) and you have a serious weight-related health problem, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or severe sleep apnea. In some cases, if your BMI is 30 to 34 and you have serious weight-related health problems, you may qualify for certain types of weight loss surgery.
But gastric bypass is not suitable for all people who are severely overweight. You may need to meet certain medical guidelines to qualify for weight loss surgery. You will likely go through an extensive screening process to see if you qualify. You must also be willing to make permanent changes to live a healthy lifestyle. You may be asked to participate in long-term follow-up programs that include monitoring of your diet, lifestyle and behavior, and medical conditions.
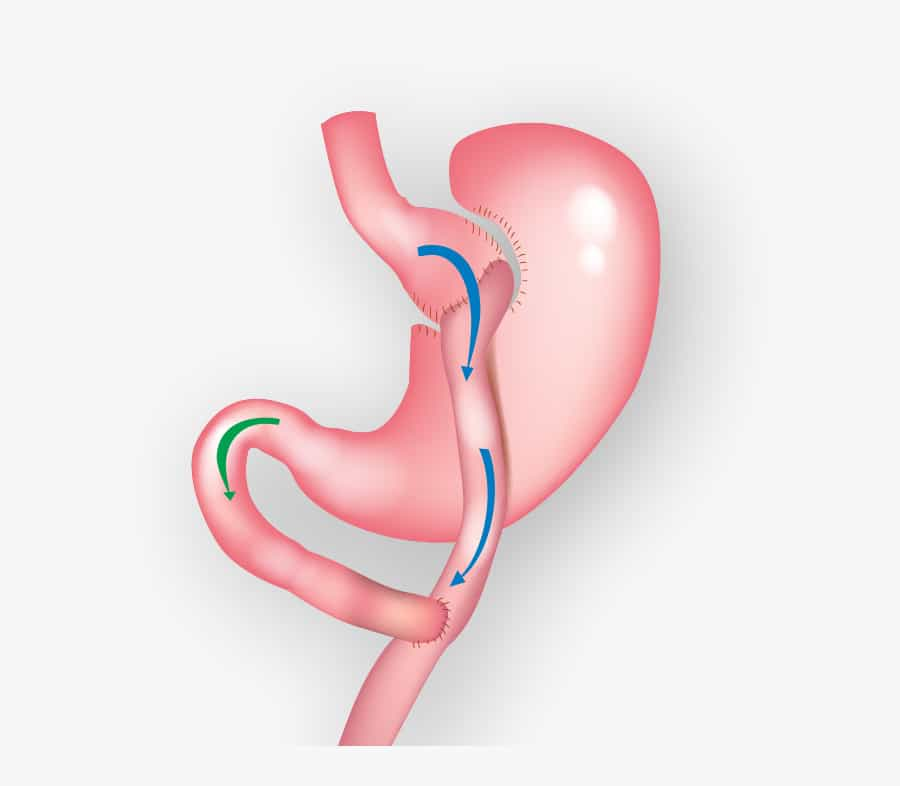
Before the surgery, you will be given general anesthesia. Anesthesia is a medicine that keeps you asleep and comfortable during surgery. The specifics of your gastric bypass will depend on your individual condition and your doctor’s actions. Some surgeries are performed through traditional large (open) incisions in your abdomen. However, most are performed laparoscopically, which involves inserting instruments through several small incisions in the abdomen. After making open or laparoscopic incisions, the surgeon will cut the top of your stomach and close it off from the rest of your stomach. The resulting pouch is about the size of a walnut and holds only about an ounce of food. Normally, your stomach can hold about 3 cups of food. The surgeon then cuts the small intestine and sews part of it directly onto the pouch. The food then goes into this small pouch in the stomach and then directly into the small intestine where it is sewn to. Most of the food bypasses your stomach and the first part of the small intestine and instead goes straight into the middle part of the small intestine. Surgery usually takes a few hours. After surgery, you will wake up in the recovery room, where the medical staff will monitor you for any complications.
Immediately after gastric bypass surgery, you may have liquids but no solid food as your stomach and intestines begin to heal. Then you’ll follow a special diet that slowly transitions from liquids to pureed foods. After that, you can eat soft foods, then move on to harder foods as your body can tolerate them. You may have many restrictions or restrictions on how much and what you can eat and drink. Your doctor will recommend that you take vitamin and mineral supplements after surgery, including a multivitamin containing iron, calcium, and vitamin B-12. You will also have frequent medical examinations to monitor your health in the first few months after weight loss surgery.
You may need laboratory tests, blood tests, and various examinations. You may experience changes as your body reacts to rapid weight loss in the first three to six months after gastric bypass surgery, including:
- body pain
- You feel tired, like you have the flu
- Feeling cold
- dry skin
- Thinning of hair and hair loss
- Mood changes
Gastric bypass can cause long-term weight loss. The amount of weight you lose depends on the type of surgery and changes in your lifestyle habits.
You may lose 70% or more of your excess weight within two years. In addition to weight loss, gastric bypass may improve or reverse conditions often associated with excess weight, including:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Type 2 diabetes
- Stroke
- infertility
Gastric bypass can also improve your ability to perform normal daily activities, which can help improve your quality of life.