What tips should you know before going to the doctor?
Weight loss surgery, also called bariatric or metabolic surgery, is used as a treatment for obese and very obese people. This surgery can lead to significant weight loss and improve many obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes. 2, high blood pressure, high blood fat, metabolic syndrome, back and joint pain, etc., but it should be noted that bariatric surgery is a major surgery and in most cases it should be done only after trying to Consider losing weight through a healthy diet and exercise.

What is body Mass Index (BMI)?
Body mass index (BMI) is a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. BMI is an inexpensive and easy screening method for weight classification including underweight, healthy weight, overweight and obesity.
BMI does not directly measure body fat, but BMI has moderate correlations with more direct measures of body fat. Furthermore, BMI appears to be equally associated with various metabolic and disease outcomes.

Now that we are familiar with the concept of body mass index or BMI, let’s see who can do bariatric surgery:
People with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or more
Between 35 and 40 and an obesity-related disease that may improve with weight loss (such as type 2 diabetes or high blood pressure)
Those who have tried all other weight loss methods such as diet and exercise, but they have not resulted in weight loss.
Types of obesity surgeries
There are different types of weight loss surgery. They are all usually performed under general anesthesia using laparoscopic surgery, but each works in a slightly different way.
Laparoscopy surgery is where the surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a flexible tube so he can see inside the abdomen during the procedure.
Gastric bypass
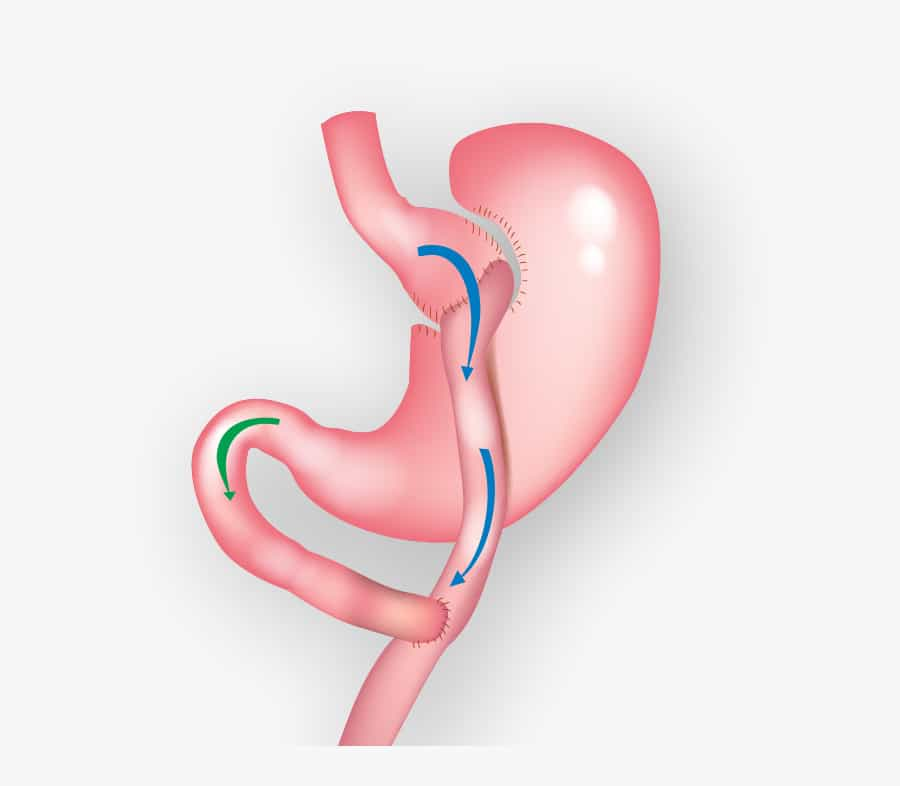
Gastric bypass is where surgical staples are used to create a small pouch at the top of the stomach.
The bag is then attached to your small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach (by passing).
This means that it takes less food to make you feel full and you absorb fewer calories from the food you eat.
Sleeve gastrectomy
A sleeve gastrectomy is where a large part of the stomach is removed, so it is much smaller than before.
This means that you will not be able to eat as much as you could before surgery and you will feel full sooner.

Gastric band
A gastric band is a band that is placed around the stomach and creates a small pouch upwards.
It takes less food to fill the bag, so you feel full by eating less food
The band is attached to a small device under the skin (usually near the middle of the chest). In this way, the band can be tightened after surgery.
The bandage is usually tightened for the first time about 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. This is done by injecting a saline solution into the device using a needle that is passed through your skin. You usually don’t need anesthesia for this.
The bandage should be tightened several times to reach the ideal tightness for you
Biliopancreatic bypass
Biliopancreatic bypass is similar to gastric bypass, except that the gastric pouch is attached more along the small intestine.
This means you will absorb even fewer calories from the food you eat. But it can cause more side effects than gastric bypass, so it is less commonly used.
Intragastric balloon
An intragastric balloon is a soft balloon filled with air or saline that is inserted into your stomach using a thin tube passed down your throat (known as a gastroscopy).
This means you won’t need or can’t eat enough before you feel full. But this is only a temporary measure and the balloon usually stays in for up to 6 months.
